一、日志文件的重要性
故障排查與問(wèn)題定位
-
快速發(fā)現(xiàn)問(wèn)題:日志能夠?qū)崟r(shí)記錄系統(tǒng)運(yùn)行過(guò)程中的各種事件和狀態(tài)信息。當(dāng)系統(tǒng)出現(xiàn)故障或異常時(shí),通過(guò)查看日志可以迅速察覺(jué)問(wèn)題發(fā)生。例如,服務(wù)器突然崩潰,日志中可能會(huì)記錄崩潰前的錯(cuò)誤信息和異常堆棧,幫助運(yùn)維人員第一時(shí)間了解系統(tǒng)故障。
-
精準(zhǔn)定位根源:詳細(xì)的日志可以提供問(wèn)題發(fā)生時(shí)的上下文信息,如函數(shù)調(diào)用順序、變量值等。以數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)連接失敗為例,日志可能記錄數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)的連接地址、端口、用戶(hù)名和密碼驗(yàn)證情況等,幫助開(kāi)發(fā)人員精準(zhǔn)定位是配置問(wèn)題、網(wǎng)絡(luò)問(wèn)題還是數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)本身的問(wèn)題。
系統(tǒng)監(jiān)控與性能分析
-
監(jiān)控系統(tǒng)狀態(tài):通過(guò)對(duì)日志的實(shí)時(shí)分析,可以監(jiān)控系統(tǒng)的運(yùn)行狀態(tài)。例如,記錄系統(tǒng)的CPU使用率、內(nèi)存占用情況、網(wǎng)絡(luò)流量等信息。一旦這些指標(biāo)超出正常范圍,日志會(huì)及時(shí)反映出來(lái),以便管理員采取相應(yīng)措施,如增加服務(wù)器資源或優(yōu)化代碼。
-
性能瓶頸分析:日志可以記錄每個(gè)操作的執(zhí)行時(shí)間,通過(guò)分析這些時(shí)間數(shù)據(jù),可以找出系統(tǒng)的性能瓶頸。比如,在一個(gè)Web應(yīng)用中,通過(guò)日志可以發(fā)現(xiàn)某個(gè)API接口的響應(yīng)時(shí)間過(guò)長(zhǎng),從而對(duì)該接口的代碼進(jìn)行優(yōu)化,提高系統(tǒng)的整體性能。
安全審計(jì)與合規(guī)性
-
安全事件追蹤:日志能夠記錄用戶(hù)的操作行為,包括登錄、數(shù)據(jù)訪問(wèn)、權(quán)限變更等。當(dāng)發(fā)生安全事件,如數(shù)據(jù)泄露或非法登錄時(shí),可以通過(guò)查看日志追蹤事件的源頭和過(guò)程,確定是否存在內(nèi)部人員違規(guī)操作或外部攻擊。
-
滿(mǎn)足合規(guī)要求:許多行業(yè)和地區(qū)都有相關(guān)的法規(guī)和標(biāo)準(zhǔn),要求企業(yè)對(duì)系統(tǒng)操作和數(shù)據(jù)進(jìn)行記錄和審計(jì)。例如,金融行業(yè)的PCI-DSS標(biāo)準(zhǔn)、醫(yī)療行業(yè)的HIPAA法規(guī)等。詳細(xì)的日志記錄可以幫助企業(yè)滿(mǎn)足這些合規(guī)要求,避免因違規(guī)而面臨的法律風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。
二、日志文件的簡(jiǎn)單實(shí)現(xiàn)
-
comm.hpp
comm.hpp 用于建立信道,Init類(lèi)用于建立命名管道和退出時(shí)自動(dòng)銷(xiāo)毀命名管道。
#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <String> #include <cerrno> #include <cstring> #include <cstdlib> #include <sys> #include <sys> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> <p>//命名管道文件路徑</p><h1>define FIFO_FILE "./myfifo"</h1><p>//文件權(quán)限</p><h1>define MODE 0664</h1><p>//枚舉命名管道錯(cuò)誤 enum{ FIFO_CREATE_ERR = 1, FIFO_DELETE_ERR, FIFO_OPEN_ERR };</p><p>class Init{ public: Init() { // 創(chuàng)建命名管道 int n = mkfifo(FIFO_FILE, MODE); if (n == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(FIFO_CREATE_ERR); } } ~Init() { //銷(xiāo)毀命名管道 int m = unlink(FIFO_FILE); if (m == -1) { perror("unlink"); exit(FIFO_DELETE_ERR); } } };
-
log.hpp
log.hpp 中存放的是日志的真正實(shí)現(xiàn),將來(lái)可以在編寫(xiě)代碼的過(guò)程中使用這個(gè)文件來(lái)將錯(cuò)誤信息打印到日志上。
#pragma once</p><h1>include <iostream></h1><h1>include <time.h></h1><h1>include <stdarg.h></h1><h1>include <sys></h1><h1>include <sys></h1><h1>include <fcntl.h></h1><h1>include <unistd.h></h1><h1>include <stdlib.h></h1><h1>define SIZE 1024</h1><p>//錯(cuò)誤等級(jí)</p><h1>define Info 0 //無(wú)錯(cuò)誤</h1><h1>define Debug 1 //需調(diào)試</h1><h1>define Warning 2 //警告</h1><h1>define Error 3 //錯(cuò)誤</h1><h1>define Fatal 4 //危險(xiǎn)</h1><p>//打印信息放到哪</p><h1>define Screen 1 //屏幕</h1><h1>define Onefile 2 //一個(gè)文件</h1><h1>define Classfile 3 //多個(gè)文件</h1><h1>define LogFile "log.txt"</h1><p>class Log{ public: Log() { //初始狀態(tài)下我們把日志打印到屏幕上 printMethod = Screen; path = "./log/"; }</p><pre class="brush:php;toolbar:false">//可以通過(guò)該函數(shù)對(duì)日志打印模式改變 void Enable(int method) { printMethod = method; } //將上面的錯(cuò)誤等級(jí)轉(zhuǎn)化為字符串 std::string levelToString(int level) { switch (level) { case Info: return "Info"; case Debug: return "Debug"; case Warning: return "Warning"; case Error: return "Error"; case Fatal: return "Fatal"; default: return "None"; } } //日志打印函數(shù) void printLog(int level, const std::string &logtxt) { //選擇打印模式 switch (printMethod) { //選擇屏幕就把信息打印出來(lái) case Screen: std::cout << levelToString(level) << " " << logtxt << std::endl; break; case Onefile: //將信息寫(xiě)入單個(gè)文件 break; case Classfile: //將信息寫(xiě)入多個(gè)文件 break; } } //打印到單個(gè)文件 void printOneFile(const std::string &filename, const std::string &logtxt) { //實(shí)現(xiàn)將信息寫(xiě)入單個(gè)文件 } //打印到多個(gè)文件 void printClassFile(int level, const std::string &logtxt) { //實(shí)現(xiàn)將信息寫(xiě)入多個(gè)文件 } //格式化日志輸出 void formatLog(int level, const char *format, ...) { time_t now = time(0); struct tm *ctime = localtime(&now); char leftbuffer[SIZE]; snprintf(leftbuffer, sizeof(leftbuffer), "[%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d] %s", ctime->tm_year + 1900, ctime->tm_mon + 1, ctime->tm_mday, ctime->tm_hour, ctime->tm_min, ctime->tm_sec); va_list s; va_start(s, format); char rightbuffer[SIZE]; vsnprintf(rightbuffer, sizeof(rightbuffer), format, s); va_end(s); char logtxt[SIZE * 2]; snprintf(logtxt, sizeof(logtxt), "%s %sn", leftbuffer, rightbuffer); printLog(level, logtxt); }
三、測(cè)試用例
#include "log.hpp"</p><h1>include <cstdlib></h1><h1>include <unistd.h></h1><p>int main(){ Log log; int cnt = 10; log.Enable(Onefile); while (cnt--) { log.printOneFile("log","i am super little monstern"); log.printClassFile(0,"this is 1n"); log.printClassFile(1,"this is 2n"); log.printClassFile(2,"this is 3n"); log.printClassFile(3,"this is 4n"); log.printClassFile(4,"this is 5n"); } return 0; }
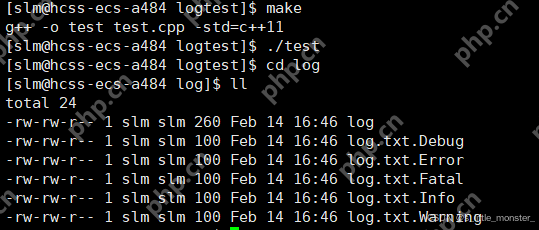
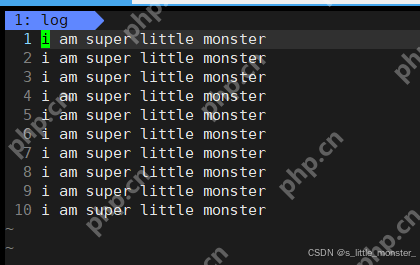
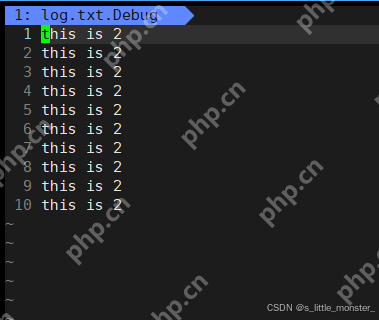
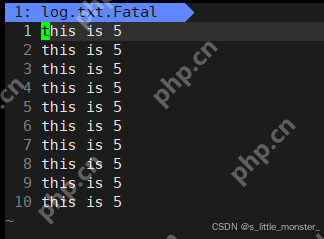
今日分享就到這里了~





.png)
費(fèi)推廣.jpg)